I am interested in the basic physics of optics, and it provides useful information on choice of equipment and settings. Diffraction plays an important part in image quality, and its importance is becoming increasingly relevant as high density sensors are becoming more widely used. So, I thought I would briefly present a few ideas, which the experts will know but may be of use to those getting into the subject.
The rays of light from a point source of light are diffracted by a circular aperture to form a series of circular rings with the major light intensity in the centre, which is called an Airy disk. The radius of the disk is given by: 1.22 x wavelength of light x f-number. For green light, radius ~ 0.5 x f microns. The point of light is smeared by diffraction, and the size of the disk is of the order of the size of pixels in digital sensor, which are in the region of 2-7 microns. The smearing increases with increasing f-number of a lens. At wide apertures of lenses, their resolution is usually limited by optical defects. At narrow apertures, diffraction is the limiting factor of resolution.
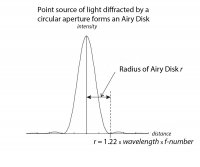
The rays of light from a point source of light are diffracted by a circular aperture to form a series of circular rings with the major light intensity in the centre, which is called an Airy disk. The radius of the disk is given by: 1.22 x wavelength of light x f-number. For green light, radius ~ 0.5 x f microns. The point of light is smeared by diffraction, and the size of the disk is of the order of the size of pixels in digital sensor, which are in the region of 2-7 microns. The smearing increases with increasing f-number of a lens. At wide apertures of lenses, their resolution is usually limited by optical defects. At narrow apertures, diffraction is the limiting factor of resolution.

