When you purchase through links on our site, we may earn an affiliate commission. Here's how it works. |
The Japanese Journal of Applied Physics has published a Canon Inc. paper on a global shutter entitled “A 3.4 μm pixel pitch global shutter CMOS image sensor with dual in-pixel charge domain memory” by Masahiro Kobayashi, Hiroshi Sekine, Takafumi Miki, Takashi Muto, Toshiki Tsuboi, Yusuke Onuki, Yasushi Matsuno, Hidekazu Takahashi, Takeshi Ichikawa, and Shunsuke Inoue.
From the paper:
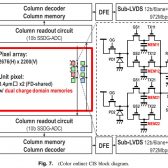
In this paper, we describe a newly developed 3.4 μm pixel pitch global shutter CMOS image sensor (CIS) with dual in-pixel charge domain memories (CDMEMs) has about 5.3 M effective pixels and achieves 19 ke− full well capacity, 30 ke−/lxcenterdots sensitivity, 2.8 e- rms temporal noise, and −83 dB parasitic light sensitivity. In particular, we describe the sensor structure for improving the sensitivity and detail of the readout procedure. Furthermore, this image sensor realizes various readout with dual CDMEMs. For example, an alternate multiple-accumulation high dynamic range readout procedure achieves 60 fps operation and over 110 dB dynamic range in one-frame operation and is suitable in particular for moving object capturing. This front-side-illuminated CIS is fabricated in a 130 nm 1P4M with light shield CMOS process.
I don't speak or truly understand the language of physics, but Richard over at Canon News does and has a broken this paper down to make it a bit more understandable for us scientific mortals.